30/10/20 What are the differences between memory cards available on Unipi e-shop differ and which applications are the individual types suitable for? This guide contains answers to all these questions.
Unipi Neuron and Unipi 1.1 controllers are based on the Raspberry Pi computer that uses microSD memory cards as its memory storage. On Unipi e-shop, you can find three types of memory cards - pSLC, MLC and SLC. Each type offers different features and this article will tell you all the important info about their operation principle, mutual differences and biggest advantages.
How do memory cards work?
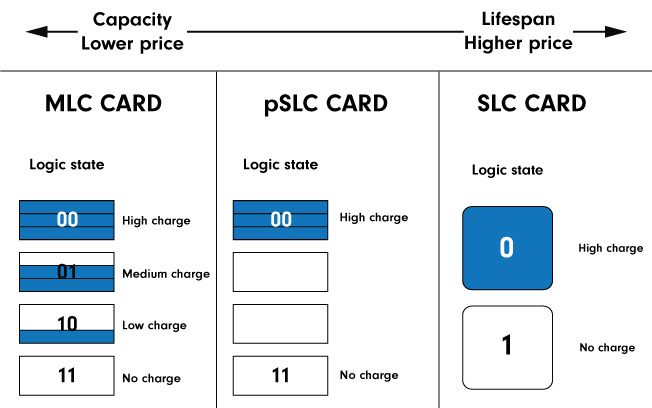
To describe the differences between the individual architectures, it is necessary to at least briefly explain the working principle of memory cards. Cards store data in memory blocks that consist of a network of memory cells. When data is written onto the card, an electric charge is stored in memory cells. This charge determines the cell’s logic state - 0 with the charge and 1 without it. In default state (a new card or erased memory block), all cells have logic state 1 and switch to state 0 during the data write. That means each memory block is erased during each rewrite.
pSLC memory card architecture can be described as a combination of MLC and SLC technologies (see below). From a technical point of view, the pSLC card is an MLC-type card whose memory cells emulate the SLC architecture by using only two outer logic states. That gives them up to five times the lifespan of MLC cards at the cost of reduced memory capacity while reducing the cost by up to 50% compared to SLC cards.
| 8GB Swissbit S-56u pSLC memory card | |
 |
Parameters -memory capacity: 8 GB operating temperature: -25/+85°C read performance: 95 MB/s write performance: 83 MB/s lifespan: up to 20 000 rewrites an option to approximate the remaining lifespan |
| Display on e-shop | |
In MLC cards, each memory cell can have more logic states as it can contain two or more data bits. As a result, MLC cards can offer significantly higher memory capacity for a lower price. On the other hand, memory blocks are sensitive to memory cell wear, resulting in a lifespan of around 3000 rewrites. After the expiration of this lifespan, it is strongly recommended to replace the card with a new one.
| 32GB microSD memory cards | |
 |
Parameters - Memory capacity: 32 GB - operating temperature: -25/+85°C - write speed: 10 - 20 MB/s - read speed: 50 - 100 MB/s |
| Display on e-shop | |
Memory cells of SLC cards can store only a single data bit and can have only two logic states (0/1). That reduces the memory capacity and increases the cost of SLC cards, but both of these disadvantages are compensated by significantly increased lifespan in the range of tens of thousands rewrites and an extended operating temperature range.
| 2GB Apacer Industrial microSD 1 SLC memory card | |
 |
Parameters -memory capacity: 2 GB operating temperature: -40/+85°C write performance: max. 43 MB/s read performance: max. 41 MB/s lifespan: up to 60 000 rewrites an option to approximate the remaining lifespan |
| Display on e-shop | |
Why is the choice of a suitable memory card important?
Aside from its architecture, the memory card’s lifespan is also influenced by its application. For example, using cheaper MLC cards in installations with frequent memory rewrites (typically storing data in a database) or high/low temperatures may result in notable lifespan decrease. Power outages during the data write can then cause instant data corruption or even total loss. Both SLC and pSLC cards are protected against such hazards. Based on these facts, we highly recommend considering the conditions the card will be used in and your expectations before the purchase.
| SLC card | pSLC card | MLC card | |
| Capacity | Up to 32 GB | Up to 32 GB | Up to 64 GB |
| Lifespan (number of rewrites) |
Up to 60 000 | Up to 20 000 | Up to 3000 |
| Data write time (microseconds) |
400 μs | 400-500 μs | 1400 μs |
| Price | Highest | Moderate | Lowest |
| Suitable for | Industrial automation and other applications in demanding conditions | All applications with increased reliability demands | Small household projects, education installation, prototyping, application development |
Can be memory card lifespan monitored?
Most available pSLC and SLC cards (including the pSLC card on the Unipi e-shop) provide operating data that can be used to approximate the remaining lifespan. This allows you to replace a worn-out card in advance, preventing any data corruption or data loss. An upcoming article will elaborate on this functionality further.
Typical MLC cards do not feature such functionality. However, their lifespan (and the lifespan of controllers as well) can be notably prolonged by following a couple of simple tips.
- in case of a need for frequent memory rewrites, use a cloud database or local NAS storage instead. For development and prototyping, you can also use an external SSD drive connected to the PLC via USB ports. In this case, the memory card serves only as operating system storage.
- do not place the controller in an environment with high or low temperatures,
- make sure there are no power fluctuations or outages.
Memory cards in Unipi products
The memory card models listed above can be purchased either as standalone products or as a part of the package:
- Unipi Neuron line: memory cards are an optional part of the package,
- Unipi 1.1/Unipi 1.1 Lite: memory card is included in the Unipi 1.1 and Unipi 1.1 Lite complete sets,
- Unipi Patron line: memory cards are not required, the controllers feature an onboard memory.